Glossary

<h1>Battery aging<h1>
Battery aging is defined as the performance or health of a battery tends to deteriorate or diminish gradually due to irreversible physical and chemical changes that take place with usage.
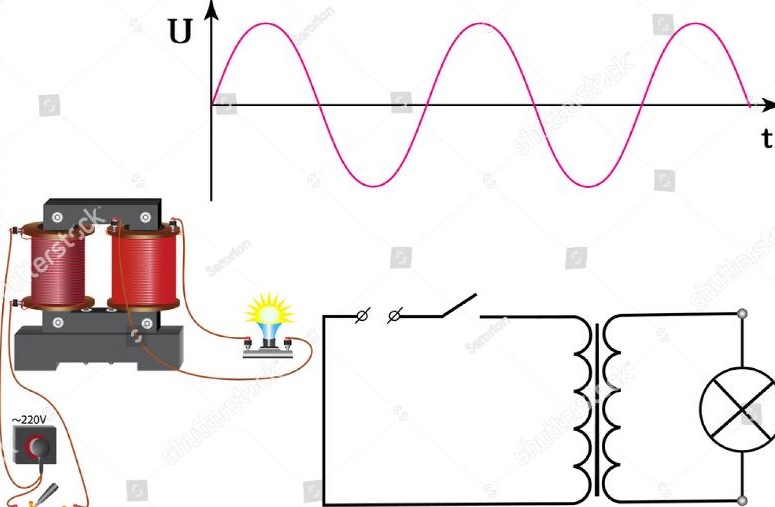
AC (Alternating Current)
A charge of electricity that regularly changes direction, which is the kind of power that comes from the power plant to homes and businesses.

AER (All-Electric Range)
The range that the EV is able to reach solely using electricity.

Alternative Fuel Vehicle
This term is used for a vehicle that runs on a fuel other than traditional petrol or diesel. It includes engines that don't solely rely on petroleum such as PHEV, EV, FCEVS, but also includes HEVs.

Ammonia-hydrogen fuel cell
An ammonia-hydrogen fuel cell is a type of fuel cell that uses ammonia (NH3) as a fuel to generate electricity
.jpg)
Autonomous Rail Transit (ART)
ART represents autonomous, trackless tram or light rail system. The construction and drive train has similarities to a regular tram but it can drive on streets and does not require rails.
.jpg)
Autonomous Vehicle (AV)
Vehicle which does not require a driver – or at least assists the driver depending on the level of automation.

Battery
Most electric vehicles, whether hybrid or all-electric in nature, require a battery to store electricity when it is not being driven and then tap into this supply when it hits the road.

Battery Capacity
The capacity of the battery, expressed in kilowatt hours (kWh), will determine the range it can cover from a single charge. The higher the capacity, the greater the distance the vehicle will be able to travel before it needs to be plugged in again.

Battery Electric Vehicle (BEV)
A car that runs purely on electric power, stored in an on-board battery that is charged from mains electricity (typically at a dedicated charge point).



