Glossary

Decarbonization
The process by which countries or other entities aim to achieve a low-carbon economy, or by which individuals aim to reduce their consumption of carbon.
.jpg)
Demand-Responsive Transport (DRT)
A form of transport where vehicles adjust their routes and/or times based on a customer’s demand rather than using a fixed route and timetable. Depending on the allowed flexibility DRT systems allow door-to-door transport. DRT is commonly used for on-demand Shared Shuttle Services.
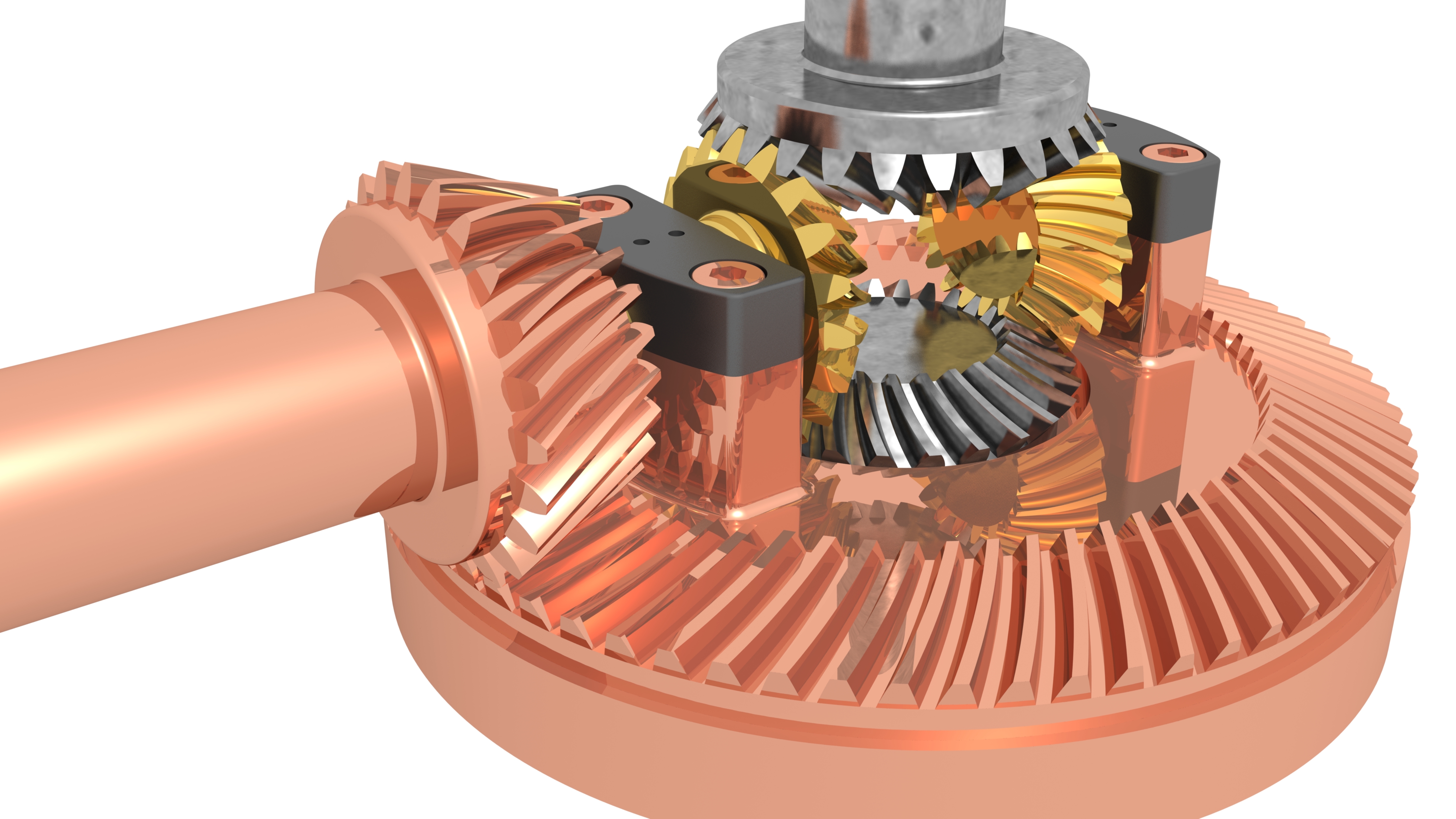
Differential Gears
Making differential gears for electric vehicles is essential as without these components, it would be impossible to turn corners smoothly. They account for the changes in wheel speed needed to make turns, since the inside wheels will be covering less distance than the outer set in this context.

Direct Current (DC)
A charge of electricity that flows in one direction and is the type of power that comes from a battery.

Dual-motor powertrain
A Dual-motor powertrain refers to a system that uses two electric motors instead of one to power the wheels.
Dynamic Ride Sharing
Ride Sharing offered in real time and on-demand usually via smart phone apps in contrast to pre-booked rides.

Ecological Footprint
The ecological footprint is a metric that measures the amount of biologically productive land and sea area needed to provide the resources a person or population consumes and to absorb the waste they generate.

Electric Motor
While a petrol or diesel-powered car will have a combustion engine at its heart, in the world of e-mobility, the electric motor is king. The most affordable, efficient vehicles will rely on a single electric motor, while higher performance models can rely on two or more motors of this type. Some even have one motor per wheel, although this is a rarity at the moment.
In terms of design, electric motors have the advantage of being far more durable and easier to maintain than combustion engines.

Electric Vehicle (EV)
Vehicle powered by electricity instead of a combustion engine. EVs may include battery-powered vehicles as well as fuel cell-powered vehicles using e.g. hydrogen as fuel. Sometimes also Hybrid Vehicles are also subsumed under EVs, which is not strictly meeting the definition. Only if powered with regenerative energy, EVs can be considered carbon-neutral in operations (not including production and disposal).
.jpg)
Electric Vehicle Battery (EVB)
An electric-vehicle battery (EVB) (also known as a traction battery) is a battery used to power the electric motors of a battery electric vehicle (BEV) or hybrid electric vehicle (HEV). These batteries are usually rechargeable (secondary) batteries, and are typically lithium-ion batteries.



