Hybrid Engine Technology
Inventor/Assignee: Ferdinand Porsche
Description:
Introduction: A hybrid electric vehicle (HEV) is a type of hybrid vehicle and electric vehicle that combines a conventional internal combustion engine (ICE) propulsion system with an electric propulsion system (hybrid vehicle drivetrain). The presence of the electric powertrain is intended to achieve either better fuel economy than a conventional vehicle or better performance. There are a variety of HEV types, and the degree to which each functions as an electric vehicle (EV) varies as well. The most common form of HEV is the hybrid electric car, although hybrid electric trucks (pickups and tractors) and buses also exist.
HEVs combine the benefits of gasoline engines and electric motors. They can be designed to meet different goals, such as better fuel economy or more power. HEVs can be either mild or full hybrids, and full hybrids can be designed in series or parallel configurations. There are four different levels of hybridization available in vehicles namely Micro hybrids, Mild hybrids, Full hybrid and Series hybrid.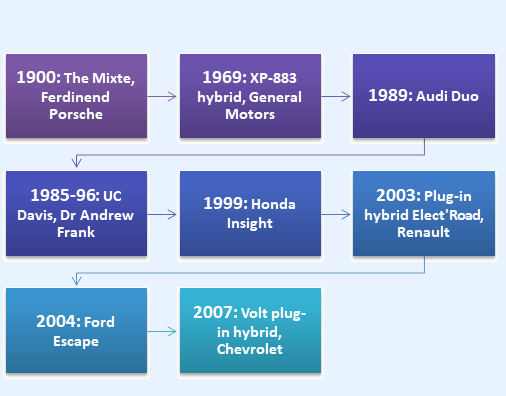
Advantages:
- Environmentally friendly
- Financial benefits
- Less dependence on fossil fuels
- Regenerative braking system
- Built from light materials
- Assistance from electric motor
- Smaller engines
- Automatic start and stop
- Electric-only drive
- Higher resale value
Limitations:
- Less power
- Expensive
- Poorer handling
- Higher maintenance costs
- Accident from high voltage in batteries
- Battery replacement is cost intensive
- Battery disposal and recycling
- Hydrogen fuel cell issues
Process: Most hybrids use several advanced technologies:
Regenerative Braking: Regenerative braking recaptures energy normally lost during coasting or braking. It uses the forward motion of the wheels to turn the motor. This generates electricity and helps slow the vehicle.
Electric Motor Drive/Assist: The electric motor provides power to assist the engine in accelerating, passing, or hill climbing. This allows a smaller, more-efficient engine to be used. In some hybrids, the electric motor alone propels the vehicle at low speeds, where gasoline engines are least efficient.
Automatic Stop/Start: Automatically shuts off the engine when the vehicle comes to a stop and restarts it when the accelerator is pressed. This reduces wasted energy from idling.
With the gradual development of HEV, new requirements are put forward for the development of hybrid technology. The key technologies include the following aspects:
- Advanced internal combustion engine technology
- Battery storage technology
- Hybrid control unit technology
- Simulation Technology
Type of Hybrid Vehicles:
- Parallel Hybrid: In this most common design, the electric motor(s) and gasoline engine are connected in a common transmission that blends the two power sources. That transmission can be an automatic, a manual, or a continuously variable transmission (CVT). One very popular hybrid transmission is a power-split CVT, which is used by the Toyota Prius and Chevrolet Volt. Transmission type and the size of the gasoline engine are the main factors that determine how a parallel hybrid will accelerate, sound, and feel. Brands that use the parallel design include Toyota, Lexus, Hyundai, Kia, Ford, Honda, Lincoln, Nissan, and Infiniti.
- Series Hybrid: In this design, the electric motor(s) provides all the thrust, and there is never a physical mechanical connection between the engine and the wheels. The gasoline engine is just there to recharge the battery. The BMW i3 with the range extender is an example of a series hybrid.
- Plug-In Hybrid: A plug-in hybrid enhances the conventional hybrid concept with a much larger battery pack that, like an electric car's, must be fully recharged using an external electricity source from your home, office, or public charging station. It allows for extended all-electric driving and can significantly reduce fuel consumption.
Commercialization:
Toyota: Camry Hybrid, Avalon Hybrid, Highlander Hybrid, Prius, etc.
Ford: C-Max Hybrid, Fusion Hybrid SE, and Fusion Energi SE.
Volvo: Volvo XC 90, Volvo XC 60, Volvo V 90, Volvo V 60, and Volvo S 90. Volvo hybrid truck and bus product lines include Volvo FE, Volvo 7900 hybrid bus, and 8400 hybrid city bus.
Daimler: Offers hybrid passenger cars, truck, and buses. Some examples of passenger hybrid cars include C-class saloon C 350e and E class saloon E 350e.
Honda: Honda Accord Hybrid, Honda Clarity Plug-In Hybrid, Honda CR-Z Hybrid, and Honda Civic Hybrid.
Nissan, Hyundai/Kia, VW/Audi/Porsche, BMW, Subaru, and Mercedes have all recently introduced variants of a single-motor, twin-clutch hybrid system, commonly referred to as a P2 hybrid.
General Motors: Uses a mild hybrid system3 that replaces the conventional alternator with a higher-power electric motor/generator and a high-tension belt drive that can work in both directions. This is commonly referred to as a belt-alternator-starter (BAS) system.
Theme: Vehicle Technology | Subtheme: Electric vehicles
Source:
Hybrid Vehicles: Technology Development and Cost Reduction, International Council on Clean Transportation, Technical Brief No. 1, July 2015
Related Documents
Books
Modern Electric, Hybrid Electric, and Fuel Cell Vehicles
Published Year: 2005
Abstract:
This book comprehensively deals in fundamentals, theory and design of conventional vehicles wi... Read More
Research Papers/Articles
Abstract:
In the modern power sector it is important to gain optimal scheduling to solve profit based un... Read More
Journals
World Electric Vehicle Journal
Published Year: 2007
Abstract:
The World Electric Vehicle Journal is the first peer-reviewed international scientific journal... Read More



