Solid-state Battery
Inventor/Assignee: Jr Donald C Freeman | Assignee: Union Carbide Corp.
Description:
Introduction: A solid-state battery is a battery technology that uses solid electrodes and a solid electrolyte, instead of the liquid or polymer gel electrolytes found in lithium-ion or lithium polymer batteries. A solid-state battery is a rechargeable energy storage system similar in overall structure and operation to the more familiar lithium-ion battery. The two differ in that a lithium-ion battery contains a liquid electrolyte while a solid-state battery features a solid one. This allows solid-state batteries to be lighter, have more energy density, offer more range, and recharge faster. Solid-state batteries can reach 80% charge within 15 minutes and incur less strain after multiple charging cycles. A solid-state battery will maintain 90% of its capacity after 5000 cycles. Automakers are making huge investments into the technology, especially with zero-emissions brand strategies and EV-only line-ups being proposed.
Maturity Timeline:

Advantages:
- Solid-state batteries are capable of delivering 2.5 times more energy density as compared to lithium-ion batteries.
- Solid-state batteries are comparatively more durable and safe.
- The solid electrolyte used in solid-state batteries is non-flammable, they are less prone to catch fire.
- Solid-state batteries are comparatively less expensive and compact.
- The greater electrochemical stability of solid-state batteries makes them more reliable.
- Solid-state batteries are comparatively lighter in weight.
- The recharge rate of solid-state batteries is 4-6 times more than regular batteries.
- A solid-state battery does not contain any volatile element.
Limitations:
- The mass production and manufacturing of solid-state batteries are quite complex.
- Research regarding solid-state batteries is still in progress, and the perfect material for the electrolyte with an ideal ionic conductivity is yet to be found.
Performance:
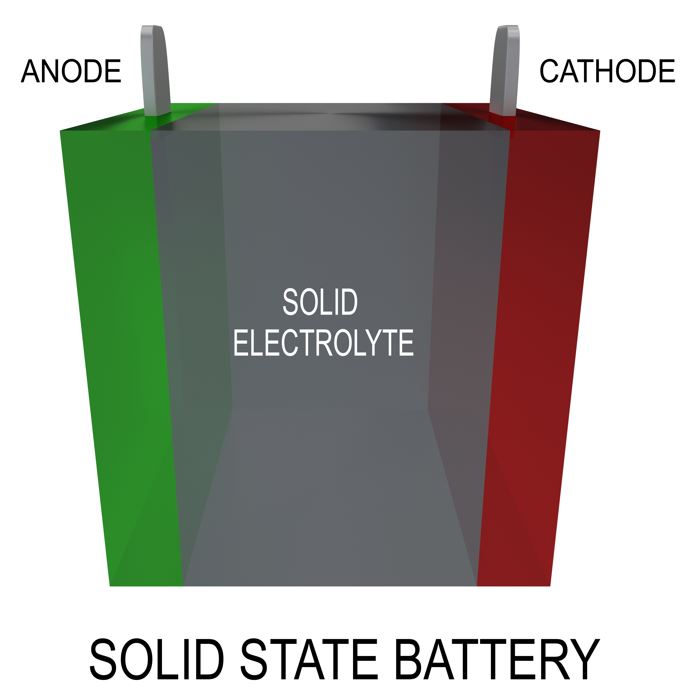
A solid-state battery makes use of solid electrodes as well as solid electrolytes. The solid electrolytes include oxides, sulfides, phosphates, polyethers, polyesters, nitrile-based, polysiloxane, polyurethane, etc. The performance of the battery depends on the type of electrolyte used. Ceramics are suitable for rigid battery systems due to their high elastic moduli, while low elastic moduli of polymers make them fit for flexible devices.
The anode and cathode of the battery are made up of electrically conductive materials. An electrolyte is present between the two electrodes that contain the charged ion particles. The lithium ions move through the electrolyte between the electrodes. This movement of charged particles in a particular direction produces current. When the ions move from the cathode to the anode, i.e., from the positive electrode to the negative electrode, it is said to be charging. Similarly, the movement of ions in the reverse direction, i.e., from the anode to the cathode discharges the battery and supplies the current to the load.
Price Range: The market size stood at USD 84.26 million in 2021. The Global Solid-State Battery Market size is expected to reach USD 721.35 Million by 2028.
Commercialization: Some of the prominent players in the solid state battery market include Samsung SDI Co. Ltd., Solvay, Cymbet, Robert Bosch GmbH and Saft
Use Cases: Automobile industry; Devices such as pacemakers, defibrillators and gardening equipment; Manufacturing and production industries; Aerospace and satellites
Patent: US3186875A
Theme: Battery Technology | Subtheme: Solid state batteries
Source:
Solid-state Battery Working Principle, Uses, and Advantages
Toyota to Spend $13.5 bln to Develop Electric Vehicle Battery Tech by 2030
Solid State Battery Market Size, Share & Trends Analysis Report
Related Documents
Research Papers/Articles
Abstract:
Read More
Research Papers/Articles
Battery Electric and Plug-in Hybrid Vehicle Uptake in European Cities
Published Year: 2023
Abstract:
This paper analyses the electric vehicle (EV) uptake and public charging infrastructure at the... Read More



