Digital Library on Green Mobility : Window to a sustainable future
Sectoral integration of the transport and energy sectors is crucial to reach the goals of Paris Agreement and low carbon transportation. This requires the development of effective policies and programmes while promoting a shared understanding between stakeholders on promising ways to transition to a decarbonised transport system. The market for electric mobility has witnessed rapid growth in recent years. Advancements in electric mobility technology with significant reductions in battery prices and improvement in efficiencies will lead to increased adoption of electric vehicles (EVs).
Integrated decision making is a prerequisite for decarbonising the transport system in an economically viable manner. This would mean bringing multiple agencies together on a common platform that will benefit the diverse stakeholders in the entire EV ecosystem to gain knowledge. This sets the basis for development of a knowledge platform that caters to diverse set of stakeholders such as government ministries, departments and agencies, civil society organizations, academia, citizens, research community, industry, businesses houses, consultants, and others.
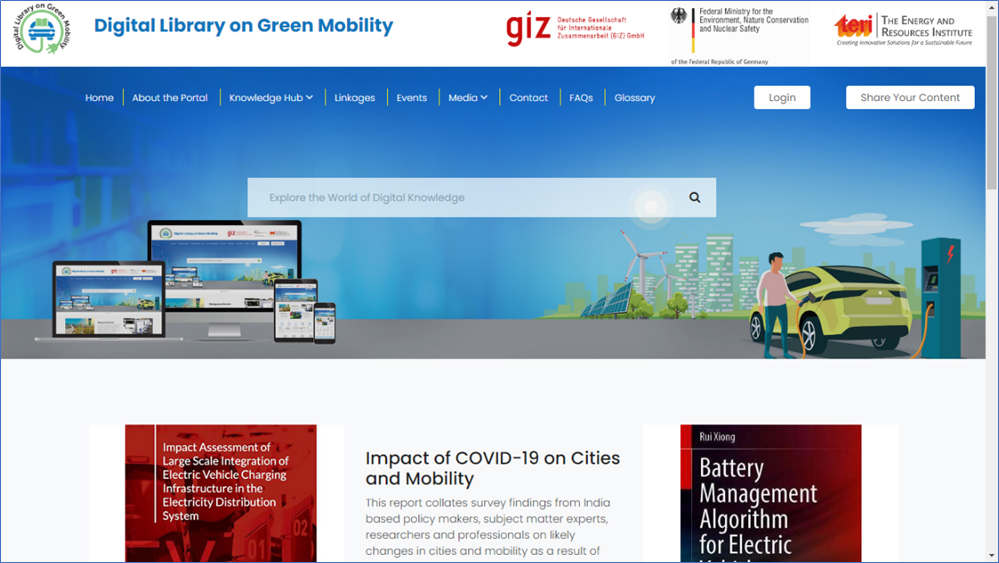
The Digital Library on Green Mobility (DLGM) has been developed under the India component of Nationally Determined Contributions -Transport Initiative for Asia (NDC-TIA) programme. The NDC-TIA was initiated with the aim to promote a comprehensive approach to decarbonize transport in India, Vietnam, and China. The project is coordinated by Deutsche Gesellschaft für Internationale Zusammenarbeit (GIZ) GmbH and funded by the German Federal Ministry for the Environment, Nature Conservation and Nuclear Safety (BMU) under the International Climate Initiative (IKI). The NDC-TIA India Component intends to support the development of policies and regulations to promote EV charging infrastructure uptake and facilitate wide-scale adoption of EVs in India. DLGM is a digital platform that comprises a set of searchable databases and links to various stakeholder organisations, accessible through different devices such as PCs, mobile phones, and tablets. Information is organized based on resource types that include Knowledge Hub, Media, Linkages, Events and Glossary. The key strength of the digital library is its use of subject based themes and sub-themes on various aspects of green mobility. All information in the portal is tagged with a comprehensive taxonomy of subject terms that makes search and retrieval of resources more accurate, relevant and contextual.
- Policies and regulations
- Research papers and articles
- Books
- Case studies
- Reports
- Journals
- Standards
- Training materials
- Opinions and viewpoints
A notable feature of the Knowledge Hub is the integration of multiple databases which give users the ability to search across content type, theme, sub-theme, tags, author, publication source, and country of origin. Users can sort search results further based on chronological order and date of publication. One of the key components of DLGM is allowing the stakeholders to share relevant resources which can be uploaded on the website.
Launch of DLGM
Launching DLGM on November 2, 2020, Dr Winfried Damm, Head of Indo-German Energy Programme, GIZ, said that lifetime and ownership costs of EVs were decreasing fast, coupled with increase in number of EVs, especially in developed nations. However, there were some obstacles for public, academia, administration, entrepreneurs, etc to adopt EVs and the online library would become the vehicle to promote green mobility in India.
Speaking at the launch of DLGM, Dr Ajay Mathur, DG, TERI, said that electric vehicles were by far the most practical vehicle technology intervention to address rising air pollution in Indian cities. The lack of cohesion between the key actors was limiting the faster adoption of EVs. With rising renewables in India’s power mix, the impact of EVs would soon be the best pathway for addressing India’s transport NDCs. It was, therefore, essential to capture the important lessons learned for future decision-making process. The DLGM, being developed by TERI, seeks to capture such learnings and best practices that would go a long way in promoting green mobility.

Mr M. Vijay Kumar, Joint Adviser, Transport, NITI Aayog highlighted the key goals of India’s NDCs to reduce GHG emission intensity of its GDP by 33-35% by 2030, from its level in 2005, as well as several initiatives taken by the Government of India to promote green mobility. Digital initiatives like DLGM were much needed for good governance, knowledge sharing, awareness and ease of doing business, observed Mr Kumar at the virtual event.